What are surgical masks used for?
Surgical masks were invented in the early 1900s, to minimize infection of surgical wounds from wearer-generated bacteria, that’s why surgical masks are also called medical procedure masks.
Table of contents
According to the CDC’s (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) guidance in infection control: Covering sneezes and coughs and placing masks on coughing patients are proven means of infection source containment that prevent infected persons from dispersing respiratory secretions into the air. And CDC also recommends that healthcare personnel should wear surgical masks while providing certain patient care or treatment, to protect themselves and those high-risk patients.
The WHO (World Health Organization) also suggested that we should wear a properly fitted mask to prevent COVID-19, “if we are at high-risk, or in crowded or poorly ventilated areas.“
So, wearing surgical masks can control the source and cut the transmission route of respiratory infectious diseases, it can protect healthcare workers, patients, as well as the public.
How do surgical masks work?
“Placing surgical masks should be effective in decreasing the risk of transmission of pathogens contained in large respiratory droplets (e.g., influenza virus, 23 adenovirus, 111 B. pertussis 827 and Mycoplasma pneumonia.” As the CDC claims in the “Infection Control > Isolation Precautions“
How do surgical masks block pathogens?

1. Physical barrier
The 3 ply structure of the surgical masks itself is a physical barrier, especially the melt-blown non-woven fabric in the middle layer is made of ultra-fine (0.5-1μm) fibers and has a dense structure between fibers, so they can block most of the large and small particles, as well as part of the pathogens.
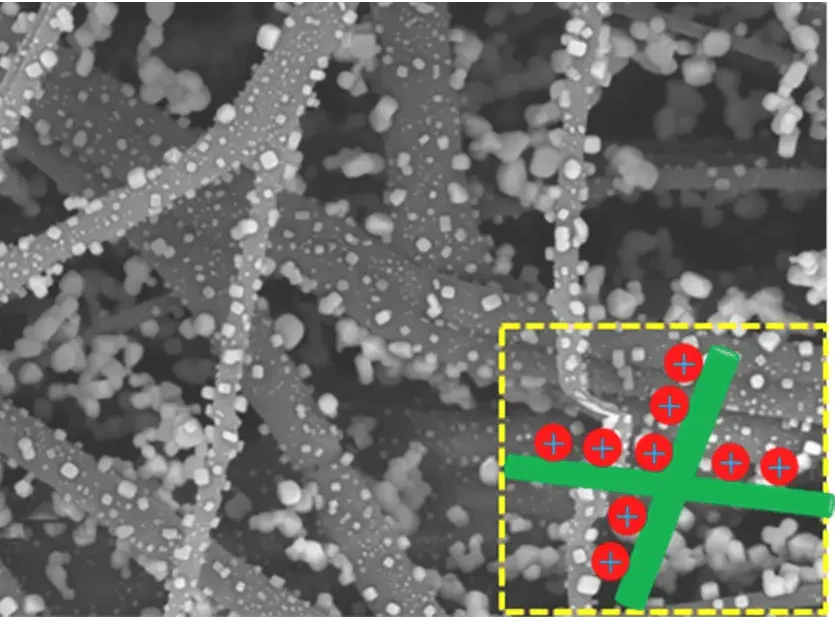
2. Electrostatic adsorption
The melt-blown fabric also plays the role of a filtering layer of a disposable mask. After going through an electrostatic electret processing, the melt-blown fibers will get a large number of electrostatic. When particles like dust, droplets, bacteria, and viruses approach, they will be absorbed by the charged fibers. This is how surgical masks filter pathogens.
What can surgical mask filter or block?
| Country | China | European Union | United States | |||||
| Product | Disposable medical masks ¹ | Surgical masks ² | Medical mask, surgical masks or procedure masks | Surgical, isolation, dental, or medical procedure masks | ||||
| Scope | Disposable masks – cover the user’s mouth, nose, and jaw, and are used in general medical environments to block exhaled or sprayed pollutants from the oral and nasal cavities. | Disposable medical masks – worn by medical staff in medical procedures and invasive operations that contain potential risks of blood, body fluid, and secretion contamination. | Medical Masks – intended to limit the transmission of infective agents from staff to patients during surgical procedures and other medical settings with similar requirements, and can effectively reduce the emission of infective agents from the nose and mouth of an asymptomatic carrier or a patient with clinical symptoms. | Medical face masks – used in providing healthcare services such as surgery and patient care. | ||||
| Standard | YY/T 0969-2023 (Latest) | YY 0469-2023 (Latest) | EN 14683-2019 | ASTM F2100 | ||||
| TypeⅠ | Type Ⅱ | Type ⅡR | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||
| PFE | Not required | ≥80% | Not required | ≥95% | ≥98% | ≥98% | ||
| BFE | ≥95% | ≥98% | ≥95% | ≥98% | ≥98% | ≥95% | ≥98% | ≥98% |
| Differential Pressure | ≤40Pa | ≤60Pa | ≤40Pa | ≤40Pa | ≤60Pa | <49Pa | <59Pa | |
| Blood Penetration | Not required | ≥16kPa | Not required | ≥16kPa | ≥10.7kPa | ≥16kPa | ≥21.3kPa | |
| Microbiological Index | ≤30 cfu/g | ≤30 cfu/g | Not required | |||||
| Flammability | Not required | ≤5 seconds The masks should burn no more than 5 seconds after leaving the flame. | Not required | Class 1 (≥3 seconds) The masks must withstand exposure to a burning flame (within a specified distance) for three seconds. | ||||
| Certification Required | 1. Medical device production license 2. Product registration certificate | CE | FDA 510K | |||||
Using Staphylococcus aureus (0.8μm) as the challenge organism to measure the BFE (bacterial filtration efficiency) of medical face masks, is all the same in China, Europe, and the US. However, the standard for medical masks in China is ≥95%, and surgical masks ≥98%. Europe and the United States are divided into three levels, from ≥95% to ≥98%.
As for PFE (Particle Filtration Efficiency), China and the US use aerosol testing, while Europe has no clear regulations on it. PFE requirements for surgical masks in China is ≥80%, while the United States divides it into three levels: Level 1 ≥95%, Level 2 ≥98% and Level 3 ≥98%.
Can surgical mask block pm2.5?
According to the EPA’s definition: PM2.5 describes fine inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 2.5 μm and smaller. Then we found the following data at the Yale Peabody Museum: Viruses are microscopic; they range in size from about 20 to 400 nm(0.04 μm) in diameter. The smallest bacteria are about 400 nm(0.04 μm).
Compared with bacteria or viruses, PM2.5 is way too much larger. So, if surgical masks (disposable procedure masks) can prevent viruses and bacteria, of course, they can block PM2.5.
However, it has to be said that surgical masks are mainly used by medical professionals for infection control, they are not designed to protect against PM2.5 particles. When you are wearing a surgical mask, you can probably feel that your breath can leak from the edges of the surgical mask. So, for particle protection like PM2.5 or dust, protective masks like N95 respirators or FFP2 respirators are more recommended.
Difference between surgical masks and n95 respirators?

Surgical Mask - Earloop

N95 Respirator Mask
1. Purpose
Surgical mask: intended to be worn by medical personnel or patients with clinical symptoms in healthcare settings, to limit the transmission of infective agents between medical staff and patients.
N95 respirator: is a filtering facepiece respirator, a piece of personal protective equipment designed for respiratory protection, that can achieve a very close facial fit and very efficient filtration of airborne particles.
2. Filtration Efficiency
Surgical mask: Some countries(like China and the United States) require their surgical mask must have certain particle filtration efficiency(PFE). But for most countries, the PFE of a surgical mask is not the focus, bacterial filtration efficiency(BFE) is.
N95 respirator: is capable of filtering out at least 95% of airborne particles, including large and small particles. But, the N95 standard does not set any requirements for BFE.
3. Fit & Seal
Surgical mask: Surgical masks are loose-fit, the edges of the masks are not designed to form a seal around the nose and mouth.
N95 respirator: can achieve a very close facial fit, the edges of the respirator are designed to form a seal around the nose and mouth. And N95 respirators should be fit-tested before use.
4. Reuse and Dispose
Surgical mask: is not intended to be reused, and if it is damaged or soiled, or if breathing through the mask becomes difficult, it should be removed, and replaced with a new one. Also, the used mask must be safely discarded.
N95 respirator: As long as it is not used in a medical environment and the air tightness of the mask is not destroyed, N95 masks can be reused. There are no special requirements for used mask disposal.
5. Breathability
Surgical masks: Typically surgical mask is more breathable than N95 respirator due to its loose fit and its 3-4 ply structure.
N95 respirators: To filter small particles, usually N95 masks are made of more than 5 layers of fabric, much thicker than surgical masks. What’s more, the perfect face seal makes they are more challenging to breathe through.
What is surgical N95 mask?
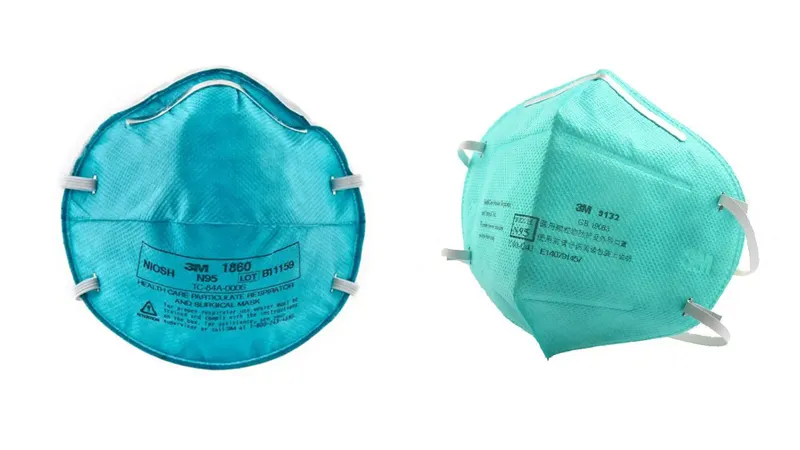

Surgical N95 respirator, also called surgical N95 mask, is a new protective mask concept that emerged after the outbreak of the epidemic in 2020. This kind of mask makes up for the poor air-tightness of surgical masks, which can reduce the risks of occupational exposure for healthcare workers.
Surgical N95 respirator is still a type of N95 filtering facepiece respirator, but also fulfills the standard of the surgical mask standard ASTM F2100. This means surgical N95 respirators need to be registered with both the FDA and the NIOSH, before launching on the US market.